In the modern business world, the main reason projects fail is neither technical failure nor a lack of budget. The primary reason is the inability to react to change on time. While traditional management methods require planning years in advance, the market changes every single day. It is within this chaos that Scrum emerges as a savior.
Scrum is not just a "collection of meetings." It is a revolutionary framework designed to help teams solve complex problems, increase productivity, and most importantly, deliver value to the customer. In this article, we will analyze the unseen sides of Scrum, how to implement it correctly, and what to avoid.
1. Why Scrum? (Waterfall vs. Agile)
To understand Scrum, you first need to understand what it opposes. In the past, projects were managed using the "Waterfall" method: 1. Analyze -> 2. Design -> 3. Code -> 4. Test. In this model, the client only saw the product 6-8 months later, when the work was finished. If they didn't like the result, everything had to start over—which meant huge losses.
Scrum says otherwise: "Don't wait 8 months. Give me 2 weeks, and I will show you a working part of the product. If you don't like it, we will change it immediately." This approach minimizes risks and ensures transparency.
2. The "3-5-3" Golden Rule of Scrum
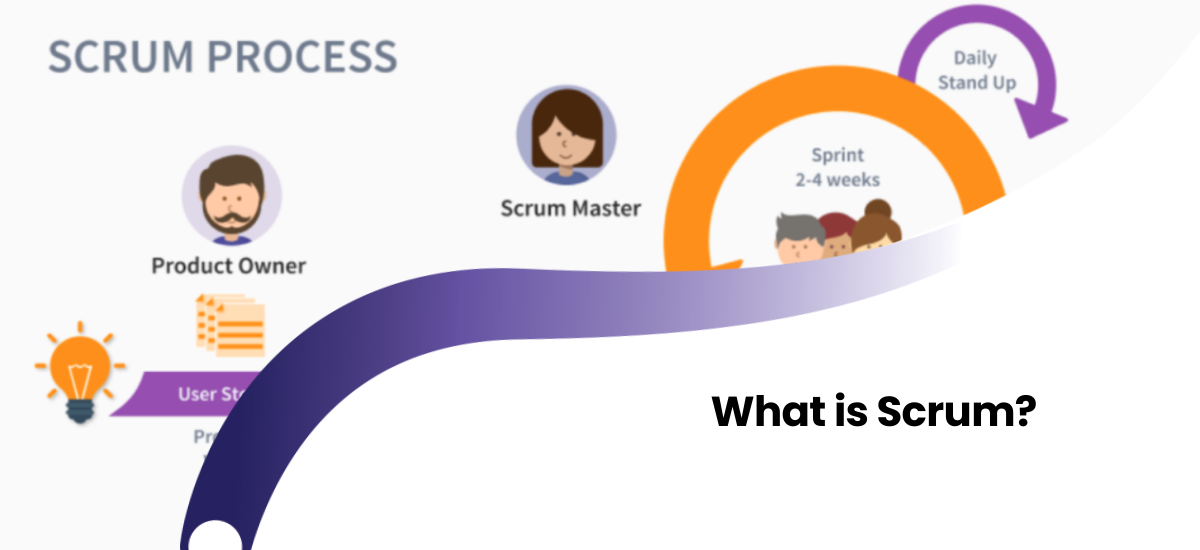
Although the Scrum methodology seems simple, its skeleton relies on strict discipline. To remember the system, the "3-5-3" formula is used: 3 Roles, 5 Events, 3 Artifacts.
A. 3 Main Roles (Team Structure)
In Scrum, there is no "Boss" or "Project Manager" in the traditional sense. Roles are divided as follows:
- Product Owner: They define "WHAT" the team will do. They are the voice of the customer. Their goal is to ensure the team spends time not on busy work, but on features that bring the most profit/value. They manage the Backlog.
- Scrum Master (Servant Leader): They monitor "HOW" the team works. The Scrum Master is not a boss, but a coach. They remove obstacles in the team's path, ensure Scrum rules are followed, and protect the team from outside interference.
- Development Team: Designers, programmers, testers. These are the professionals who execute the work and answer the questions "how much" and "by when." In Scrum, there is no hierarchy within the team; everyone is equal.
B. 3 Artifacts (Tools of Transparency)
- Product Backlog: An ordered list of everything that needs to be done in the project (wishes, requirements, bugs). This list never ends and is constantly updated.
- Sprint Backlog: A list of specific tasks to be completed only in the current cycle (e.g., in these 2 weeks).
- Increment: A working piece of the product that emerges at the end of the sprint, which works and can be shown to the customer.
3. The Scrum Process: Heartbeat of the Sprint (5 Events)
Work in Scrum is conducted in short cycles called Sprints (usually 2-4 weeks). What happens inside this cycle?
[Image of Scrum sprint cycle diagram]- Sprint Planning: Held on the first day of the sprint. The Product Owner puts the most important tasks on the table, and the team answers the question: "How much of this can we finish in 2 weeks?" As a result, a goal is defined.
- Daily Scrum: Held every morning at the same time, standing up, for a maximum of 15 minutes. The goal is not to report to management, but to synchronize with each other.
- Sprint Review: At the end of the sprint, the customer and stakeholders are invited. The team demonstrates the working product, saying, "Look at what we built in these 2 weeks." Live feedback is received.
- Sprint Retrospective: The most important but often forgotten part of Scrum. After the customer leaves, the team stays alone and discusses: "What did we do wrong? What can we improve in the next sprint?" This is the foundation of Continuous Improvement (Kaizen).
4. When Does Scrum NOT Work? (Pitfalls and Mistakes)
Scrum is not a magic wand. It may not be suitable for every project:
- Fixed Requirements: If you are building a bridge or have a precise construction plan, Scrum is not suitable—Waterfall is better. Scrum is strong where there is uncertainty.
- "Zombie Scrum": Many companies hold meetings and assign roles but do not adopt Scrum values (courage, openness, respect). This is called "Zombie Scrum"—there is the appearance of Agile, but no results.
- Micromanagement: If management interferes with the team's work every day and changes tasks, Scrum will not work. The Sprint is sacred.
5. Real Business Benefits of Scrum
Why do Google, Amazon, Spotify, and even the FBI use Scrum in their projects?
- Time-to-Market: Without waiting for the entire product to be finished, you release new features every month, staying ahead of competitors.
- High Quality: Errors are detected and fixed not at the end of the project, but at the end of every sprint.
- Customer Satisfaction: The customer is involved in the process, sees what they are getting, and faces no unpleasant surprises at the finale.
6. Tools Used
Standard digital tools for managing Scrum:
- Jira: The most popular and functional Scrum management tool.
- Trello: Kanban/Scrum board for simpler projects.
- Asana / Monday.com: Visually convenient task management systems.
Conclusion: Being Agile is a Necessity
Scrum is not just for programmers. Today, marketing agencies, HR departments, and even educational institutions plan their work using Scrum. The only way to survive in a changing world is to adapt.
Scrum does not promise you a perfect plan; it teaches you to see mistakes quickly, fix them quickly, and constantly move forward.
"Plans are nothing; planning is everything." With this philosophy, Scrum saves your projects from boring documents and turns them into living organisms.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is a Scrum Master the same as a Project Manager (PM)?
No. A PM manages the team and gives orders. A Scrum Master serves the team, removes obstacles, and ensures the process runs correctly.
How long should a Sprint last?
The standard recommendation is 2 weeks. However, depending on the project dynamics, it can last between 1 to 4 weeks.
Is Scrum only used in IT?
No. Scrum can be applied in marketing, education, manufacturing, and any other field that requires teamwork on a complex product.
 +994512060920
+994512060920